м„ң лЎ
к°‘мғҒм„ м•”мқҖ лҢҖл¶Җ분мқҖ мң л‘җм•”кіј м—¬нҸ¬м•”мқҙм§Җл§Ң, к·ё мҷё лҜёл¶„нҷ”м„ұ к°‘мғҒм„ м•” л°Ҹ мҲҳм§Ҳм•”, лҰјн”„мў… л“ұмқҙ л°ңмғқн•ҳкё°лҸ„ н•ңлӢӨ. мқҙ мӨ‘ лҜёл¶„нҷ”м„ұ к°‘мғҒм„ м•”мқҖ лӢӨм–‘н•ң л©ҙм—ӯм„ёнҸ¬н•ҷм Ғ лҳҗлҠ” мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм ҒмңјлЎң лӢӨм–‘н•ң ліҖмқҙнҳ•л“Өмқҙ мЎҙмһ¬н•ңлӢӨ. лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…(lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma)мқҖ лҜёл¶„нҷ”м„ұ к°‘мғҒм„ м•”мқҳ ліҖмқҙнҳ• мӨ‘ н•ҳлӮҳмқҙл©° к°‘мғҒм„ м—җм„ң л°ңмғқ л№ҲлҸ„лҠ” л§Өмҡ° л“ңл¬јлӢӨ. м„ём№ЁнқЎмқём„ёнҸ¬кІҖмӮ¬лҠ” к°‘мғҒм„ мў…кҙҙ нҸүк°Җм—җ мӨ‘мҡ”н•ң 진лӢЁ лҸ„кө¬мқҙм§Җл§Ң, лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҳ кІҪмҡ° м„ёнҸ¬ лӘЁм–‘мқ„ нҷ•мқён•ҳлҠ” м„ём№ЁнқЎмқём„ёнҸ¬кІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң м •нҷ•нһҲ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм§Җ лӘ»н•ҳлҜҖлЎң мҲҳмҲ м Ғмқё м Ҳм ң мғқкІҖ л“ұмқҳ л°©лІ•мқ„ нҶөн•ҙ м•”мЎ°м§Ғкіј мЈјліҖ мЎ°м§Ғкіјмқҳ нҳ•нғңлҘј кҙҖм°°н•ҳм—¬м•јл§Ң мқҙм—җ лҢҖн•ң 진лӢЁмқҙ к°ҖлҠҘн•ҳлӢӨ[1,2]. м Җмһҗл“ӨмқҖ м„ём№ЁнқЎмқём„ёнҸ¬кІҖмӮ¬лЎң мҡ°мёЎ к°‘мғҒм„ мң л‘җм•”мў…мқҙ мқҳмӢ¬лҗҳм–ҙ мҲҳмҲ мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ң 28м„ё м—¬мһҗ нҷҳмһҗм—җм„ң мҲ нӣ„ лі‘лҰ¬мЎ°м§ҒкІҖмӮ¬лЎң лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҙ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм–ҙ 추к°Җм Ғмқё л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢ мӢңн–ү нӣ„ мһ¬л°ң м—Ҷмқҙ кІҪкіј кҙҖм°° мӨ‘мқё мҰқлЎҖлҘј кІҪн—ҳн•ҳмҳҖкё°м—җ, л¬ён—Ң кі м°°кіј н•Ёк»ҳ ліҙкі н•ҳлҠ” л°”мқҙлӢӨ.
мҰқ лЎҖ
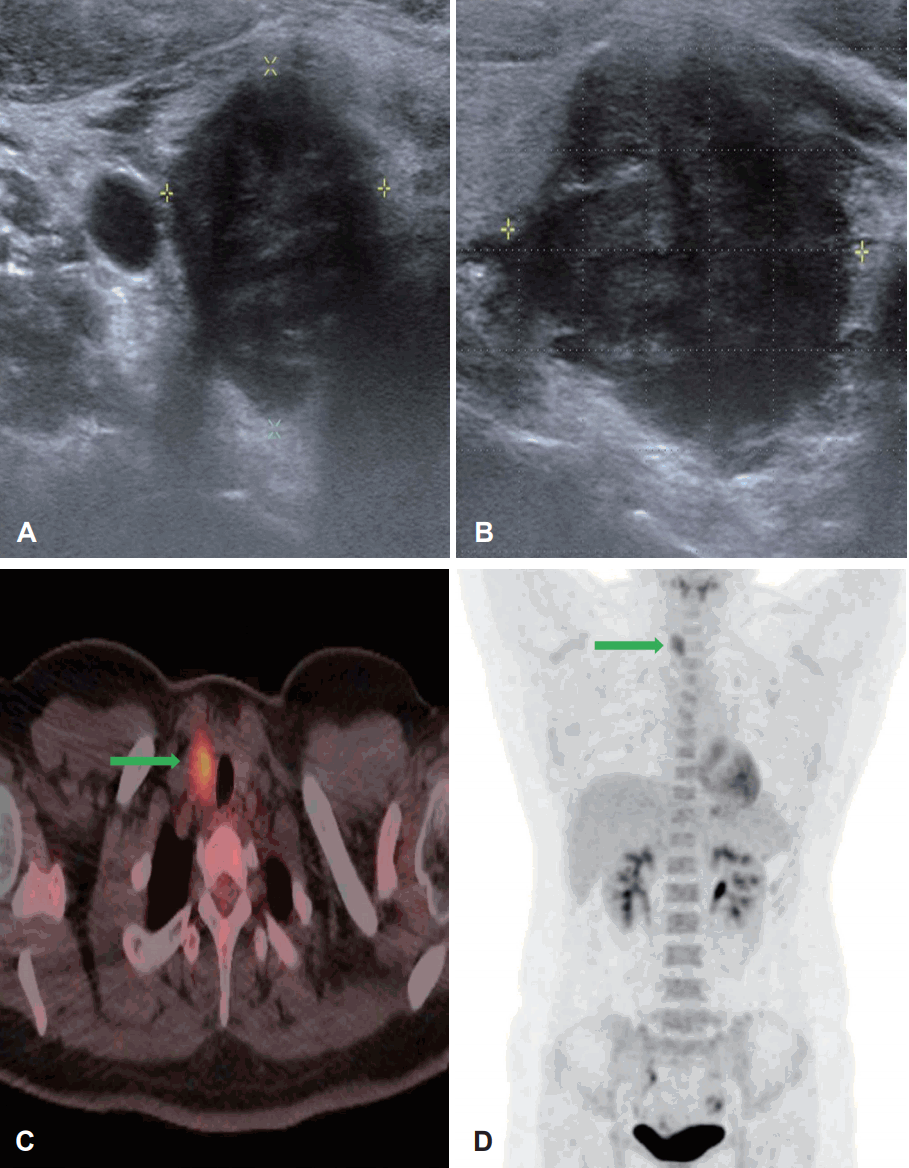
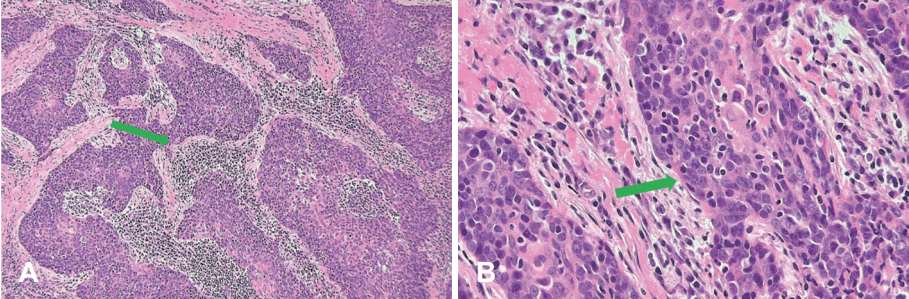
28м„ё м—¬мһҗ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ мҡ°м—°нһҲ кұҙк°• кІҖ진м—җм„ң мӢңн–үн•ң кІҪл¶Җ мҙҲмқҢнҢҢм—җм„ң мҡ°мёЎ к°‘мғҒм„ мў…л¬јмқҙ л°ңкІ¬лҗҳм–ҙ лӮҙмӣҗн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. кіјкұ°л Ҙ л°Ҹ мӢ мІҙ кІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң нҠ№мқҙ мҶҢкІ¬мқҖ м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨ. кІҪл¶Җ мҙҲмқҢнҢҢм—җм„ң 2.8Г—2.1Г—1.9 cm нҒ¬кё°мқҳ м Җм—җмҪ” лҢҖ분м—Ҫнҷ”лҗң м•…м„ұмңјлЎң мқҳмӢ¬лҗҳлҠ”(high sus-picion) кІ°м Ҳмқҙ к°‘мғҒм„ мҡ°н•ҳм—Ҫм—җм„ң нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©°, лҰјн”„м Ҳ м „мқҙ л“ұмқ„ мқҳмӢ¬н•ҳлҠ” мҶҢкІ¬мқҖ м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨ. к°‘мғҒм„ кІ°м Ҳм—җ мӢңн–үн•ң м„ём№ЁнқЎмқём„ёнҸ¬кІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң к°‘мғҒм„ мң л‘җм•”мў… мҶҢкІ¬(Bethesda system VI)мқ„ BRAF мң м „мһҗ кІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ңлҠ” мқҢм„ұ мҶҢкІ¬мқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ(Fig. 1A and B). кІҪл¶Җ м „мӮ°нҷ”лӢЁмёөмҙ¬мҳҒм—җм„ң мЈјліҖ лҰјн”„м Ҳ 비лҢҖлҠ” м—Ҷм—Ҳкі м–‘м „мһҗл°©м¶ңлӢЁмёөмҙ¬мҳҒм—җм„ңлҠ” кіјлҢҖмӮ¬л°ҳмқ‘мқҙ к°‘мғҒм„ мҡ°м—Ҫм—җ мһҲм—Ҳм§Җл§Ң, лӢӨлҘё мһҘкё°мқҳ м „мқҙлҠ” кҙҖм°°лҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ(Fig. 1C and D). м „мӢ л§Ҳм·Ён•ҳм—җ лЁјм Җ к°‘мғҒм„ мҡ°м—Ҫм Ҳм ңмҲ мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳм—¬ лҸҷкІ°м ҲнҺёкІҖмӮ¬лҘј мқҳлў°н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. лҸҷкІ°м ҲнҺёкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң мң л‘җм•”мқҙ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм–ҙ к°‘мғҒм„ м „м Ҳм ңмҲ мқ„ н•ҳмҳҖкі , мңЎм•Ҳм ҒмңјлЎң лӢӨмҲҳмқҳ 비лҢҖн•ҙ진 лҰјн”„м Ҳмқҙ кҙҖм°°лҗҳм–ҙ мӨ‘мӢ¬кІҪл¶ҖлҰјн”„м Ҳ мІӯмҶҢмҲ лҸ„ к°ҷмқҙ мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мҲҳмҲ мӨ‘ нӣ„л‘җмӢ кІҪ к°җмӢңлҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳм—¬ м–‘мёЎ нӣ„л‘җмӢ кІҪ л°ҳмқ‘ л°Ҹ ліҙмЎҙмқ„ нҷ•мқён•ҳмҳҖкі м–‘мёЎ мғҒ, н•ҳ л¶Җк°‘мғҒм„ лҸ„ ліҙмЎҙн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мҲ нӣ„ л©ҙм—ӯнҷ”н•ҷкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң м•”м„ёнҸ¬л“Ө мӮ¬мқҙм—җ лӢӨмҲҳмқҳ лҰјн”„кө¬к°Җ л‘ҳлҹ¬мӢём—¬ мһҲмқҢмқҙ нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©°, лі‘лҰ¬ мЎ°м§ҒкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң 2.4Г—1.7Г—1.7 cm нҒ¬кё°мқҳ мў…л¬јкіј H&E м—јмғүм—җм„ң лҰјн”„кө¬ кө°м§‘мқҙ м•”м„ёнҸ¬м—җ м№ЁмңӨн•ҙ мһҲлҠ” мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм Ғ нҠ№м§•мқҙ мһҲкі , л©ҙм—ӯнҷ”н•ҷм—јмғүм—җм„ң p63 м–‘м„ұ, CD5мҷҖ Bcl-2 мқҢм„ұкІ°кіјлЎң лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мңјлЎң нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ(Fig. 2). н”јл§үм№ЁлІ”мҶҢкІ¬мқҖ мһҲмңјлӮҳ, лҰјн”„ л°Ҹ нҳҲкҙҖ м№ЁмңӨ, мЈјліҖ лҰјн”„м ҲлЎңмқҳ м „мқҙлҠ” м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨ(0/15). м•ұмҠӨнғҖмқё-л°” л°”мқҙлҹ¬мҠӨ(Epstein-Barr virus, EBV)мҷҖ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҙ мһҲлӢӨлҠ” ліҙкі лҸ„ мһҲм–ҙ мҲҳмҲ нӣ„ мӢңн–үн•ң EBV н•ӯмІҙкІҖмӮ¬лҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©° EBV IgM мқҢм„ұ, EBV IgG м–‘м„ұ мҶҢкІ¬мқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ[1]. мҲҳмҲ мқҙнӣ„ л°©мӮ¬м„ мў…м–‘н•ҷкіј нҳ‘진н•ҳм—җ 6мЈјк°„мқҳ 6000 cGy л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј 추к°ҖлЎң мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖмңјл©°, 6к°ңмӣ” нӣ„ мӢңн–үн•ң м–‘м „мһҗл°©м¶ңлӢЁмёөмҙ¬мҳҒм—җм„ң мһ¬л°ң мҶҢкІ¬мқҙ м—Ҷм—ҲлӢӨ. мҲҳмҲ нӣ„ 32к°ңмӣ”м§ё ліёмӣҗ мҷёлһҳм—җм„ң кІҪкіј кҙҖм°° мӨ‘мқҙл©° мһ¬л°ң л°Ҹ м „мқҙмқҳ 징нӣ„лҠ” ліҙмқҙм§Җ м•Ҡкі мһҲлӢӨ.
кі м°°
лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…(lymphoepithelioma)мқҖ мЈјлЎң 비мқёл‘җм—җм„ң кё°мӢңн•ҳлҠ” м Җ분нҷ” 비мқёл‘җм•”мў…мқҙлӢӨ. мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм Ғ нҠ№м§•мңјлЎң м•”м„ёнҸ¬ л¶Җмң„м—җ лӢӨмҲҳмқҳ лҰјн”„кө¬к°Җ м№ЁмңӨн•ҳм—¬ лҰјн”„кө¬ лӮҙк°•мқ„ нҳ•м„ұн•ҳкі мһҲмңјл©°, лҰјн”„кө¬л“Өмқҙ кө°м§‘лҗҳм–ҙ мңөн•©лҗҳм–ҙ мһҲлҠ” Schmincke л°°м—ҙкіј Regaud л°°м—ҙмқ„ к°Җ진лӢӨ[2,3]. лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…(lymphoepithelioma-like carcinoma)мқҖ 비мқёл‘җ мқҙмҷёмқҳ мһҘмҶҢм—җм„ң л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ” лҜёл¶„нҷ”м„ұ м•”мў…мңјлЎң лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…мқҳ мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм Ғ нҠ№м§•мқ„ к°Җ진лӢӨ. ліё мҰқлЎҖмқҳ кІҪмҡ°м—җлҸ„ мЎ°м§ҒкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң лҰјн”„кө¬ кө°м§‘мқҙ м•”м„ёнҸ¬м—җ м№ЁмңӨн•ҙ мһҲм—Ҳмңјл©°, Schmincke л°°м—ҙкіј Regaud л°°м—ҙмқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ. лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҖ нғҖмһҘкё°м—җм„ңлҸ„ л°ңмғқн•ҳл©° к°‘мғҒм„ м—җм„ң л°ңмғқ мӢң мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм ҒмңјлЎң к°‘мғҒм„ м•”мқҳ лҜёл¶„нҷ”м•” ліҖмқҙмў…мңјлЎң 분лҘҳлҗңлӢӨ[4]. лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҳ лҜёкөӯ лӮҙ мң лі‘лҘ мЎ°мӮ¬м—җм„ң мЈјлЎң л°ұмқё, лӮЁм„ұ(1.8:1), 60м„ё лҜёл§Ңм—җ л§Һмқҙ л°ңмғқн•ңлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗңлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң л‘җкІҪл¶Җ мҳҒм—ӯм—җм„ңлҠ” кө¬мқёл‘җ л°ңмғқ비мңЁмқҙ к°ҖмһҘ лҶ’кі лӢӨмқҢмңјлЎң нғҖм•Ўм„ кё°мӣҗмқҙ л§Һм•ҳмңјл©°, лҸҷм–‘мқёкіј м—җмҠӨнӮӨлӘЁмқём—җм„ң мЈјлЎң л°ңмғқн•ңлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗңлӢӨ[5,6]. лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҖ 비мқёл‘җ мқҙмҷёмқҳ мӢ мІҙм—җм„ң л°ңмғқн•ҳм§Җл§Ң к·ё л№ҲлҸ„к°Җ л§Өмҡ° л“ңл¬јлӢӨ. мЈјлЎң нғҖм•Ўм„ , мң л°©, л°©кҙ‘, нҸҗ, мң„, н”јл¶Җ, к°„, нқүм„ , мӢқлҸ„, лҢҖмһҘ, мһҗк¶ҒкІҪл¶Җ, мһҗк¶ҒлӮҙл§ү, м „лҰҪм„ , мқҢмҲңм—җм„ң л°ңмғқн•ҳкі к°‘мғҒм„ мҳҒм—ӯм—җм„ңлҠ” н•ҙмҷём—җм„ң 4мҳҲл§Ңмқҙ л°ңн‘ңлҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©°, көӯлӮҙм—җм„ң м•„м§Ғ ліҙкі лҗң м ҒмқҖ м—ҶлӢӨ[1,4,7,8]. лӢӨлҘё к°‘мғҒм„ м•”мқҳ лҜёл¶„нҷ” м•” ліҖмқҙмў…мқҳ н•ң мў…лҘҳмқё Carcinoma Showing Thymus-Like Differentiation(CASTLE)кіј мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм Ғ мң мӮ¬м„ұмқҙ мһҲмңјлҜҖлЎң к°җлі„мқҙ н•„мҡ”н•ҳлӢӨ[9,10]. CASTLEмқҳ кІҪмҡ° EBV л©ҙм—ӯкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң мқҢм„ұ л°Ҹ p63, CD5, Bcl-2 л“ұмқҳ л©ҙм—ӯнҷ”н•ҷм—јмғүм—җм„ңлҠ” м–‘м„ұл°ҳмқ‘мқҙ лӮҳнғҖлӮҳл©°, ліё мҰқлЎҖм—җм„ң мӢңн–үн•ң л©ҙм—ӯкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ңлҠ” p63 м–‘м„ұ, CD5мҷҖ Bcl-2 мқҢм„ұ кІ°кіјлЎң л‘җ м•”мў… к°„мқҳ кө¬л¶„мқҙ к°ҖлҠҘн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ[7,11,12].
лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҖ лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…мқ„ нҸ¬н•Ён•ҳлҠ” лӢӨлҘё 비мқёл‘җм•”мў…кіј мң мӮ¬н•ҳкІҢ EBV к°җм—јкіј лҶ’мқҖ м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҙ мһҲлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗңлӢӨ. нғҖм•Ўм„ , нқүм„ , нҸҗ, мң„лҠ” EBV к°җм—јкіј лҶ’мқҖ м—°кҙҖмқҙ мһҲмңјл©°, к°‘мғҒм„ мқ„ нҸ¬н•Ён•ҳлҠ” мӢқлҸ„, мң л°©, л°©кҙ‘, н”јл¶Җ, к°„ л“ұмқҳ мһҘкё°лҠ” м—°кҙҖм„ұмқҙ лӮ®мқҖ кІғмңјлЎң м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲмңјлӮҳ, ліё мҰқлЎҖм—җм„ң мӢңн–үн•ң EBV к°җм—ј м—¬л¶Җ кІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ңлҠ” м–‘м„ұ мҶҢкІ¬мқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ[1,8,10.13].лҳҗн•ң кө¬мқёл‘җ мҳҒм—ӯм—җм„ң 40~80%мқҳ лҰјн”„м Ҳ м „мқҙк°Җ ліҙмқҙкі мқёк°„мң л‘җмў…л°”мқҙлҹ¬мҠӨ(human papillomavirus) к°җм—јлҸ„ м—°кҙҖлҗҳм–ҙ мһҲлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗңлӢӨ[14].
лҰјн”„мғҒн”јм„ұ м•”мў…мқҖ л°ңмғқ мң„м№ҳм—җ л”°лқј мҲҳмҲ , л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢ лҳҗлҠ” лі‘н•©м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӮ¬мҡ©н•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ к°ҖлҠҘн•ҳкі , мӣҗкұ°лҰ¬ м „нҢҢ к°ҖлҠҘм„ұмқ„ л§үкё° мң„н•ҙ м „мӢ м Ғмқё м•Ҫл¬ј мӮ¬мҡ©мқ„ нҶөн•ң лі‘н–үм№ҳлЈҢк°Җ к°ҖлҠҘн•ҳлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗңлӢӨ[5]. к°‘мғҒм„ мҳҒм—ӯм—җм„ңлҠ” нҳ„мһ¬к№Ңм§Җ мҲҳмҲ м Ғ м№ҳлЈҢл§Ң мӢңн–үн•ң 1мҳҲмҷҖ м•Ҫл¬јм№ҳлЈҢл§Ң мӢңн–үн•ң 1мҳҲк°Җ мһҲмңјл©°, мҲҳмҲ м Ғ м№ҳлЈҢл§Ң мӢңн–үн•ң 1мҳҲмқҳ кІҪмҡ° лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мқҙ мһ¬л°ңлҗҳм—ҲлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ[5,7,12]. ліё мҰқлЎҖм—җм„ңлҠ” лі‘лҰ¬ кІ°кіјм—җм„ң н”јл§ү м№ЁлІ” мҶҢкІ¬мқҙ мһҲкі мҲҳмҲ л§Ң н•ҳмҳҖмқ„ л•Ң мһ¬л°ңн•ң м„ лЎҖлҘј м°ёкі н•ҳм—¬ к°‘мғҒм„ м „м Ҳм ңмҲ мқҙнӣ„ 추к°Җм Ғмқё л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. м•Ҫ 32к°ңмӣ”мқҙ м§ҖлӮң нҳ„мһ¬к№Ңм§Җ мһ¬л°ңмқҳ 징нӣ„лҠ” лӮҳнғҖлӮҳм§Җ м•Ҡкі мһҲлӢӨ. к°‘мғҒм„ мқ„ м ңмҷён•ң нғҖ мһҘкё°м—җм„ң л°ңмғқн•ң лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҳ м№ҳлЈҢ нӣ„ мғқмЎҙ кё°к°„мқҖ лҸҷмқј мһҘкё°м—җм„ң кё°мӣҗн•ҳлҠ” лӢӨлҘё лҜёл¶„нҷ”м„ұ м•”мў…кіј 비көҗ мӢң, мҲҳмҲ л°Ҹ л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢк°Җ м Ғм Ҳн•ҳкІҢ мӢңн–үлҗ кІҪмҡ° 5л…„ мғқмЎҙмңЁмқҙ 70% мқҙмғҒмңјлЎң мҳҲнӣ„к°Җ мўӢлӢӨкі ліҙкі лҗңлӢӨ[4,5]. м•„м§Ғк№Ңм§Җ к°‘мғҒм„ м—җм„ң л°ңмғқн•ң лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҳ м№ҳлЈҢ нӣ„ мҳҲнӣ„лҘј мҳҲмғҒн•ҳкё°м—җлҠ” ліҙкі лҗң мҰқлЎҖк°Җ л§Һм§Җ м•ҠлӢӨ. лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҳ кІҪмҡ°, лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…мқҳ мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм Ғ нҠ№м§•мқҙ мһҲм–ҙ көӯмҶҢм Ғмқё м „нҢҢ л°Ҹ нҳҲкҙҖм№ЁлІ”, лҰјн”„м Ҳ м „мқҙ к°ҖлҠҘм„ұмқ„ л°°м ңн• мҲҳ м—ҶлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…мқҖ л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢм—җ лҢҖн•ң лҶ’мқҖ лҜјк°җлҸ„лҘј к°Җм§ҖлҠ” нҠ№м§•мқҙ мһҲмңјлҜҖлЎң лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…м—җм„ңлҸ„ мҲ нӣ„ л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј мӢңн–үн•ҳлҠ” кІғмқҙ лҚ” лӮҳмқҖ мҳҲнӣ„лҘј кё°лҢҖн• мҲҳ мһҲмқ„ кІғмңјлЎң мҳҲмғҒлҗңлӢӨ[15]. лӢӨл§Ң м•„м§Ғ лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…м—җ лҢҖн•ң мҲҳмҲ л°Ҹ л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢмқҳ кё°мӨҖмқҖ м •н•ҙм ё мһҲм§Җ м•Ҡм•„ м—°кө¬к°Җ лҚ” н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң мғқк°ҒлҗңлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң к°‘мғҒм„ лҰјн”„мғҒн”јмў…м„ұ м•”мў…мқҖ м„ём№ЁнқЎмһ…кІҖмӮ¬лЎң 진лӢЁн•ҳкё° м–ҙл ӨмӣҢ мҲҳмҲ нӣ„ л’ӨлҠҰкІҢ нҷ•м§„ лҗҳлҠ” кІҪмҡ°к°Җ л§Һм•„ 진лӢЁ мӢң мЈјмқҳк°Җ н•„мҡ”н•ҳл©°, мқҙм—җ лҢҖн•ң м№ҳлЈҢ л°Ҹ мҳҲнӣ„м—җ лҢҖн•ң м—°кө¬к°Җ лҚ” н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң мӮ¬лЈҢлҗңлӢӨ.