м„ң лЎ
м§ҒмһҘм•”мқҖ кІ°мһҘм•”кіј н•©міҗ лҢҖмһҘм•”мңјлЎң н•ңкөӯм—җм„ң 3лІҲм§ёлЎң нқ”н•ң м•”мқҙл©°[1], к°„, нҸҗ, кіЁ, лҮҢ л“ұ лӢӨм–‘н•ң мӣҗкІ© м „мқҙлҘј мқјмңјнӮӨм§Җл§Ң[2], л¶Җ비лҸҷмңјлЎң м „мқҙлҠ” л§Өмҡ° л“ңл¬јлӢӨ[3]. м „л‘җлҸҷмңјлЎң м „мқҙлҗң м§ҒмһҘм•”мқҖ м•„м§Ғ көӯлӮҙм—җм„ң ліҙкі лҗң мҳҲк°Җ м—Ҷкі , м„ңкө¬м—җм„ңлҸ„ л¬ён—Ңмқ„ м°ҫм•„ліҙкё° нһҳл“ӨлӢӨ. м Җмһҗл“ӨмқҖ м§ҒмһҘм•”мқҙ м „л‘җлҸҷмңјлЎң м „мқҙлҗҳм—ҲлҚҳ 1мҳҲлҘј кІҪн—ҳн•ҳмҳҖкё°м—җ мқҙлҘј л¬ён—Ңкі м°°кіј н•Ёк»ҳ ліҙкі н•ҳлҠ” л°”мқҙлӢӨ.
мҰқ лЎҖ
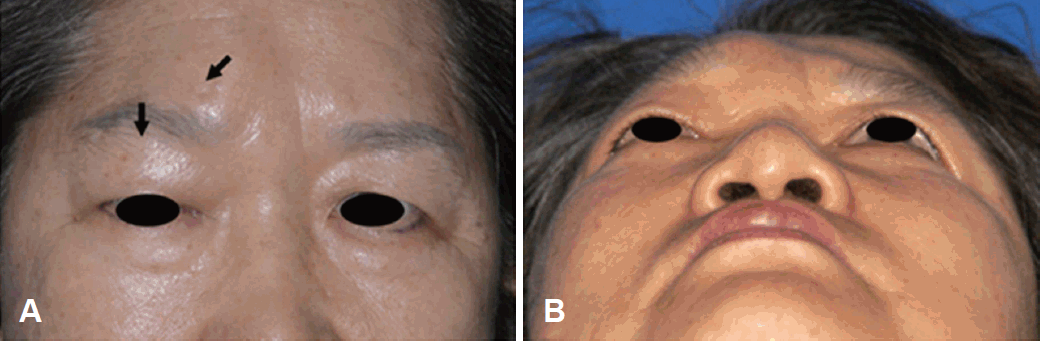
66м„ё м—¬мһҗ нҷҳмһҗк°Җ 2к°ңмӣ” м „л¶Җн„° л°ңмғқн•ң л‘җнҶөкіј м „л‘җл¶Җмқҳ мў…м°Ҫмқ„ мЈјмҶҢлЎң лӮҙмӣҗн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. кіјкұ°л ҘмғҒ нҷҳмһҗлҠ” 3л…„ м „ м§ҒмһҘм„ м•”(rectal adenocarcinoma, T3N2bM0, Stage III)мқ„ 진лӢЁл°ӣкі ліёмӣҗ мҷёкіјм—җм„ң м Җмң„м „л°©м Ҳм ңмҲ мқ„ мӢңн–үл°ӣм•ҳмңјл©° мқҙнӣ„ 12нҡҢмқҳ н•ӯм•”нҷ”н•ҷмҡ”лІ•(FOLFOX-4, oxaliplatin-based regimens) нӣ„ лӮҙмӣҗ 2л…„ м „ нҸҗмқҳ лӢӨл°ңм„ұ м „мқҙк°Җ л°ңкІ¬лҗҳм—ҲмңјлӮҳ мқҙнӣ„ 추м ҒкҙҖм°° мӨ‘ мң мқҳн•ң ліҖнҷ”лҠ” м—ҶлҠ” мғҒнғңмҳҖлӢӨ. мқҙн•ҷм Ғ кІҖмӮ¬мғҒ мҡ°мёЎ м „л‘җл¶Җмқҳ мў…м°Ҫкіј мҡ°мёЎ м•Ҳкө¬мЈјмң„ л¶Җмў… мҷё мҡ°м•Ҳмқҳ м•ҲкІҖн•ҳмҲҳк°Җ кҙҖм°°лҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©°(Fig. 1), 비лӮҙмӢңкІҪ мҶҢкІ¬мғҒ нҠ№мқҙ мҶҢкІ¬мқҖ м—Ҷм—Ҳкі кІҪл¶ҖлҰјн”„м Ҳ мў…лҢҖлҠ” мҙүм§Җлҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ.
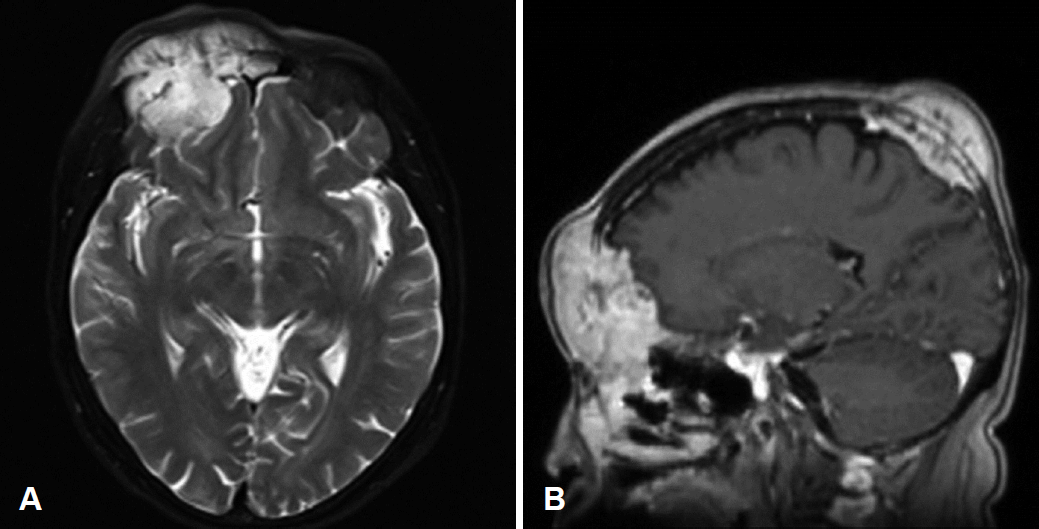
비л¶Җ비лҸҷ м „мӮ°нҷ”лӢЁмёөмҙ¬мҳҒ л°Ҹ мһҗкё°кіөлӘ…мҳҒмғҒм—җм„ң мҡ°мёЎ м „л‘җл¶ҖмҷҖ м „л‘җлҸҷ лӮҙм—җ л¶Ҳк· мқјн•ҳкІҢ мЎ°мҳҒмҰқк°•мқҙ лҗҳлҠ” мў…л¬јмқҙ кҙҖм°°лҗҳм—Ҳкі (Fig. 2), мқём ‘н•ҳкі мһҲлҠ” л‘җк°ңм ҖмҷҖ лҮҢмҲҳл§үмқ„ м№ЁлІ”н•ҳл©° мғҒмӢңмғҒ м •л§ҘлҸҷ(superior sagittal sinus)м—җм„ң л‘җм •м—Ҫк№Ңм§Җ лҮҢмҲҳл§үмқҖ л¬јлЎ л‘җк°ңкіЁ к·ёлҰ¬кі л‘җн”јк№Ңм§Җ м№ЁмҠөн•ң м–‘мғҒ(Fig. 3)мқ„ ліҙм—¬ м „мқҙм„ұ л¶Җ비лҸҷ мў…м–‘ к°ҖлҠҘм„ұмқ„ м—јл‘җм—җ л‘җкі м „мӢ л§Ҳм·Ё н•ҳм—җ лӮҙмӢңкІҪм Ғ мў…м–‘м ңкұ°мҲ мқ„ мӢңн–үн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ.
мҲҳмҲ мҶҢкІ¬мғҒ мў…кҙҙлҠ” 2.9Г—1.4Г—1.5 cmмқҳ нҒ¬кё°лЎң л¶Ҳк·ңм№ҷн•ң н‘ңл©ҙмқ„ ліҙмҳҖмңјл©° мҡ°мёЎ м „л‘җлҸҷмқҳ нӣ„л©ҙм—җ л¶ҷм–ҙ мЈјліҖ м җл§үкіј мң м°© мҶҢкІ¬мқ„ ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ. мҲ мӨ‘ мӢңн–үн•ң лҸҷкІ°м ҲнҺёмЎ°м§ҒкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң м•…м„ұ мў…м–‘мңјлЎң нҷ•мқёлҗҳм—ҲмңјлӮҳ м •нҷ•н•ң 진лӢЁмқҖ л¶Ҳк°ҖлҠҘн•ҳм—¬ мў…л¬ј 축мҶҢмҲ кіј м „л‘җлҸҷ м Ҳк°ңмҲ мқ„ мӢңн–ү нӣ„ мҲҳмҲ мқ„ мў…лЈҢн•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. мҲҳмҲ нӣ„ кІҪл¶Җ лҰјн”„м Ҳ л°Ҹ кё°нғҖ мһҘкё°лЎңмқҳ 추к°Җ м „мқҙ м—¬л¶Җ нҷ•мқёмқ„ мң„н•ҳм—¬ мӢңн–үн•ң м–‘м „мһҗл°©м¶ңлӢЁмёөмҙ¬мҳҒмғҒ кё°мЎҙмқҳ нҸҗм „мқҙмҷҖ мҡ°мёЎ м „л‘җл¶ҖмҷҖ м „л‘җлҸҷ мҷё лӢӨлҘё мһҘкё°м—җм„ңмқҳ мӣҗкІ©м „мқҙ мҶҢкІ¬мқҖ кҙҖм°°лҗҳм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ.
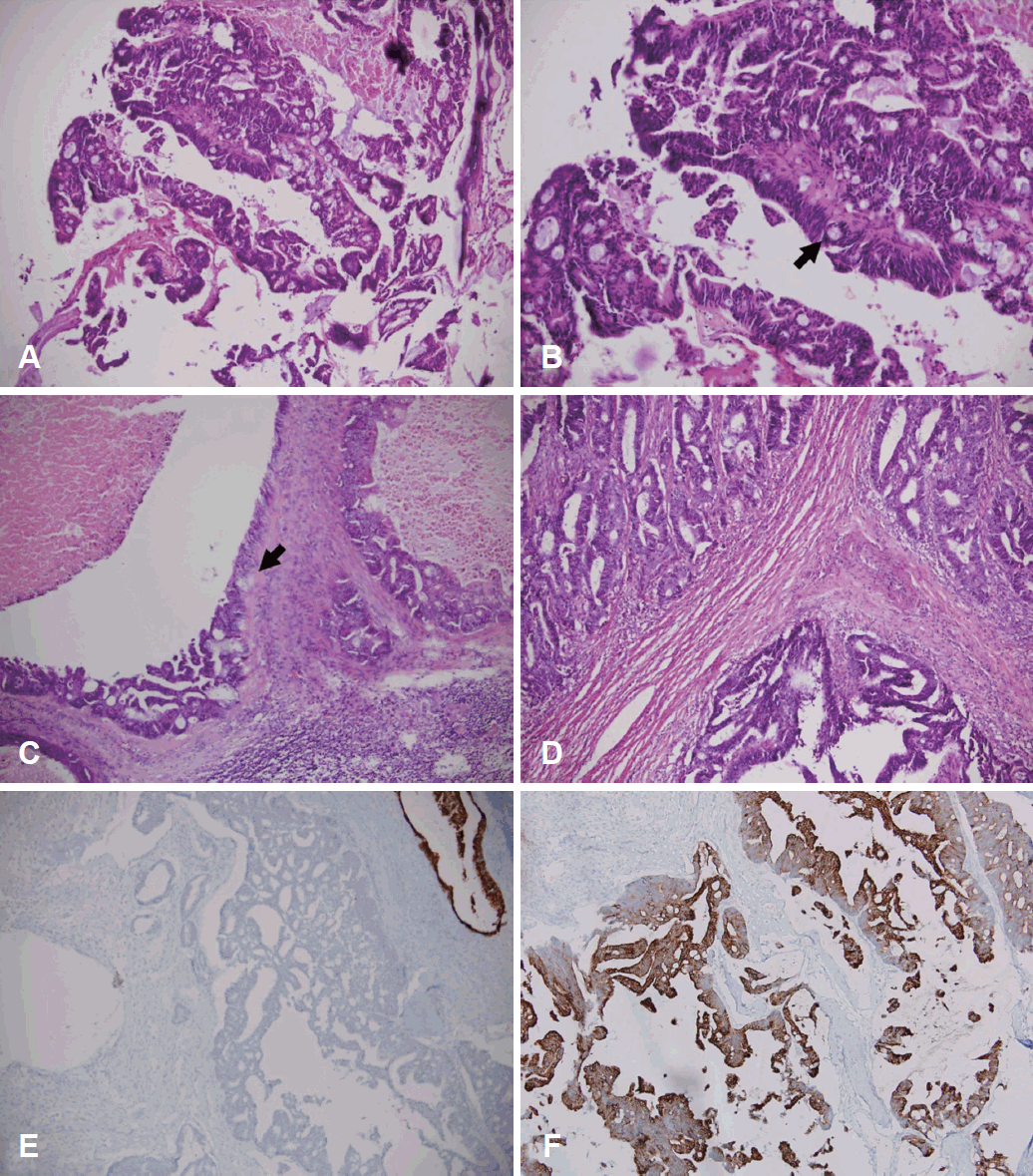
лі‘лҰ¬мЎ°м§ҒкІҖмӮ¬м—җм„ң кІ°мІҙмЎ°м§ҒмңјлЎң м№ЁмңӨн•ҳл©° ліөмһЎн•ң м„ кө¬мЎ°лҘј к°Җ진 мӨ‘л“ұлҸ„лЎң 분нҷ”лҗң мң л‘җмғҒ м„ м•”мў…мқҙ кҙҖм°°лҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©° мқҙлҠ” нҷҳмһҗмқҳ кё°мЎҙ м§ҒмһҘм•” мЎ°м§Ғ мҶҢкІ¬кіј мқјм№ҳн•ҳмҳҖкі , л©ҙм—ӯмЎ°м§Ғнҷ”н•ҷ м—јмғүм—җм„ң cytokeratin 7м—җ мқҢм„ұ, cytokeratin 20м—җ м–‘м„ұ мҶҢкІ¬мқ„ ліҙм—¬ м „мқҙм„ұ м„ м•”мў…мңјлЎң нҢҗлӘ…лҗҳм—ҲлӢӨ(Fig. 4).
мөңмў… мЎ°м§ҒкІҖмӮ¬ кІ°кіјм—җ л”°лқј л‘җк°ңм•Ҳл©ҙм Ҳм ңмҲ л°Ҹ мҳҲл°©м Ғ кІҪл¶Җ м Ҳм ңмҲ мқ„ кі„нҡҚн•ҳм—¬ к¶Ңмң н•ҳмҳҖмңјлӮҳ нҷҳмһҗлҠ” мҲҳмҲ м Ғ м№ҳлЈҢлҘј кұ°л¶Җн•ҳм—¬ мғҒкёүлі‘мӣҗмңјлЎң м „мӣҗ, мһ„мғҒмӢңн—ҳ н”„лЎңк·ёлһЁм—җ м°ём—¬н•ҳкІҢ н•ҳлҠ” л“ұ ліҙмЎ° н•ӯм•”нҷ”н•ҷмҡ”лІ•мқ„ мӢңн–үн–Ҳм§Җл§Ң м№ҳлЈҢм—җ лі„лӢӨлҘё л°ҳмқ‘мқ„ ліҙмқҙм§Җ м•Ҡм•ҳлӢӨ. нҳ„мһ¬ м •кё°м ҒмңјлЎң мҷёлһҳм—җм„ң кІҪкіј кҙҖм°° мӨ‘мқҙлӢӨ.
кі м°°
м§ҒмһҘм•”мқҖ лҢҖмһҘм—җм„ң кІ°мһҘм•”м—җ мқҙм–ҙ 2лІҲм§ёлЎң нқ”н•ң м•”мңјлЎң мқҙл“Өмқ„ н•©м№ң лҢҖмһҘм•”мқҖ лҜёкөӯм—җм„ң м•”мңјлЎң мқён•ң мӮ¬л§қ мӨ‘ 3лІҲм§ёлЎң нқ”н•ҳлӢӨ[4]. н•ңкөӯм—җм„ңлҸ„ көӯлҰҪм•”м„јн„° мһҗлЈҢм—җ л”°лҘҙл©ҙ лҢҖмһҘм•”мқҖ 3лІҲм§ёлЎң нқ”н•ң м•”мқҙл©°[1], м„ңкө¬нҷ”лҗң мӢқмҠөкҙҖ л“ұмқҳ нҷҳкІҪм Ғмқё мӣҗмқёмңјлЎң к·ё л°ңмғқ л№ҲлҸ„лҠ” кҫёмӨҖнһҲ мҰқк°Җн• кІғмңјлЎң ліҙмқёлӢӨ[5].
비л¶Җ비лҸҷмңјлЎңмқҳ мӣҗкІ©м „мқҙлҠ” л§Өмҡ° л“ңл¬јм–ҙ 1951л…„л¶Җн„° 2011л…„к№Ңм§Җ 167кұҙмқҙ мҰқлЎҖлЎң ліҙкі лҗҳм–ҙ мһҲмңјл©° к°ҖмһҘ нқ”н•ң мӣҗл°ңм•”мқҖ мӢ м„ёнҸ¬м•”мқҙл©° мғҒм•…лҸҷмқ„ к°ҖмһҘ л§Һмқҙ м№ЁлІ”н•ҳлҠ” кІғмңјлЎң м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲлӢӨ[6]. м „ м„ёкі„м ҒмңјлЎң мң„мһҘкҙҖм•”мқҳ 비л¶Җ비лҸҷ мӣҗкІ©м „мқҙлҠ” лӘЁл‘җ 8кұҙ, к·ё мӨ‘ м§ҒмһҘм•”м—җм„ңмқҳ м „мқҙлҠ” 3кұҙмқҙ ліҙкі лҗҳм—Ҳмңјл©°[3,7,8], н•ңкөӯм—җм„ңлҠ” м•„м§Ғ ліҙкі лҗң л°”к°Җ м—ҶлӢӨ.
비л¶Җ비лҸҷм—җ л°ңмғқн•ң м „мқҙм•”мқҳ мҰқмғҒмқҖ 비нҠ№мқҙм ҒмңјлЎң, 비м¶ңнҳҲ, 비нҸҗмғү, м•Ҳл©ҙнҶөмҰқ л“ұмқҳ 비мҰқмғҒмқҙлӮҳ, м•ҲкІҖн•ҳмҲҳ, ліөмӢң, мӢңл Ҙм Җн•ҳ л“ұмқҳ м•Ҳкө¬мҰқмғҒмқ„ лӮҳнғҖлӮј мҲҳ мһҲкі [6,9,10], ліё мҰқлЎҖм—җм„ңлҠ” л¶Җмў…кіј м•ҲкІҖн•ҳмҲҳлҘј ліҙмҳҖлӢӨ.
ліё мҰқлЎҖм—җм„ң м „л‘җлҸҷ м„ м•”мў…мқҳ м „мқҙм„ұ лі‘мҶҢ м—¬л¶ҖлҘј нҸүк°Җн•ҳкё° мң„н•ҳм—¬ м§ҒмһҘм•”кіјмқҳ мЎ°м§Ғн•ҷм Ғмқё мқјм№ҳм„ұ мҷё л©ҙм—ӯмЎ°м§Ғнҷ”н•ҷ м—јмғүмқ„ нҷңмҡ©н•ҳмҳҖлӢӨ. Cytokeratin 7кіј cytokeratin 20м—җм„ң лӘЁл‘җ м–‘м„ұмқё кІҪмҡ° 비л¶Җ비лҸҷм—җм„ң кё°мӣҗн•ң мһҘнҳ• м„ м•”мў…мқј к°ҖлҠҘм„ұмқҙ нҒ¬кі cytokeratin 7м—җм„ң мқҢм„ұ, cytokeratin 20м—җм„ң м–‘м„ұмқј кІҪмҡ° мһҘм—җм„ң кё°мӣҗн•ң м „мқҙм„ұ м„ м•”мў…мқј к°ҖлҠҘм„ұмқҙ нҒ°лҚ°[3,11], м Җмһҗл“Өмқҳ мҰқлЎҖм—җм„ңлҸ„ cytokeratin 20м—җм„ңл§Ң м–‘м„ұмқ„ ліҙм—¬ м „л‘җлҸҷм—җ м „мқҙлҗң м§ҒмһҘм•”мңјлЎң 진лӢЁн• мҲҳ мһҲм—ҲлӢӨ.
Tanaka [8]лҠ” мӮ¬кіЁлҸҷм—җ м „мқҙлҗң м§ҒмһҘм•”мқ„ кё°мҲ н•ҳл©° м¶”кіЁм •л§Ҙмҙқмқ„ нҶөн•ң м „мқҙ кІҪлЎңлҘј м„ӨлӘ…н•ҳмҳҖкі , к·ё мҷё л‘җкІҪл¶ҖлЎң м „мқҙлҗң м•”м—җ кҙҖн•ң лӢӨмҲҳмқҳ мҰқлЎҖ ліҙкі л“Ө м—ӯмӢң м¶”кіЁм •л§Ҙмҙқмқ„ мЈјмҡ” м „мқҙ кІҪлЎңлЎң м ңмӢңн•ҳмҳҖмңјлӮҳ[6,12,13], ліё мҰқлЎҖм—җм„ң л°ңмғқн•ң м§ҒмһҘм•”мқҳ мӣҗкІ© м „мқҙлҠ” нҸҗ м „мқҙ мқҙнӣ„м—җ м „л‘җлҸҷкіј л‘җк°ңкіЁ л“ұм—җ м „мқҙлҗң кІғмңјлЎң нҳҲн–үм„ұ лҳҗлҠ” кІҪмӮ¬мғҒнҢҗ(transcribrosal) мҷё лӢӨлҘё м „мқҙ кІҪлЎңк°Җ мһҲмқ„ кІғмңјлЎң м¶”м •лҗңлӢӨ[6,12,14].
мқҙмІҳлҹј мӣҗл°ңм„ұ м§ҒмһҘм•”мңјлЎңл¶Җн„° 비л¶Җ비лҸҷмңјлЎңмқҳ м „мқҙлҠ” л§Өмҡ° нқ¬к·Җн•ҳл©° м–ҙл– н•ң мӣҗмқёкіј кІҪлЎңлЎң м „мқҙк°Җ л°ңмғқн•ҳлҠ”м§ҖлҠ” мһҳ м•Ңл Өм ё мһҲм§Җ м•ҠлӢӨ. лҳҗн•ң 비л¶Җ비лҸҷмңјлЎң м•”мў…мқҙ м „мқҙлҗҳм—Ҳмқ„ кІҪмҡ°, 진лӢЁ мӢңм җм—җ лі‘кё°к°Җ лҶ’м•„ л°©мӮ¬м„ м№ҳлЈҢ л°Ҹ н•ӯм•” нҷ”н•ҷмҡ”лІ•кіј к°ҷмқҖ кі мӢқм Ғ м№ҳлЈҢ л°©лІ•м—җ мқҳмЎҙн•ҳкІҢ лҗҳл©° мҳҲнӣ„к°Җ мўӢм§Җ м•ҠмңјлҜҖлЎң мқҙм—җ лҢҖн•ң м—°кө¬к°Җ лҚ”мҡұ н•„мҡ”н• кІғмңјлЎң мӮ¬лЈҢлҗңлӢӨ.